MPC Node User Guide
1. Sinohope WaaS MPC Technology Introduction
Threshold Signature Scheme (TSS) is an important branch of digital signature. It is a cryptographic technology based on Secure Multi-Party Computation (MPC) and an important research direction of MPC key management.
Sinohope's WaaS (Wallet as a Service) is a wallet-as-a-service solution based on MPC-TSS technology. Sinohope's WaaS service requires customers and the platform to collaborate in a distributed manner, each holding a private key sharding. Based on the MPC-CMP protocol (ECDSA) and SS01 protocol (EdDSA), it implements customer-led off-chain multi-party signatures. MPC Node is a dedicated program package provided by Sinohope WaaS for customers to manage their own private key sharding.
Sinohope adopts a 3-3 multi-signature mode, where customers hold one private key sharding and Sinohope holds two private key sharding.
- MPC Node 1: Sinohope is responsible for management, and this Node will always be online.
- MPC Node 2: Sinohope is responsible for management, and this Node will always be online.
- MPC Node 3: The customer is responsible for management and should also keep the automated process always online.
2. MPC Node deployment and implementation
2.1 Environmental preparation
2.1.1 Common Server Environment
General-purpose servers refer to Cloud as a Service Provider EC or TCE-metal servers operated and maintained independently by customers.
Minimum configuration
- CPU: AMD64 or ARM64 architecture, 2 cores, frequency 2.0 GHz
- Memory: 4G
- Hard drive: 64G SSD
- Operating system: Ubuntu 20.04 or latest. (Note: Theoretically supports all systems that can run Docker)
Recommended configuration
- CPU: AMD64 or ARM64 architecture, 4 cores, frequency 3.0 GHz
- Memory: 8G
- Hard drive: 128G SSD
- Operating system: Ubuntu 20.04 or latest. (Note: Theoretically supports all systems that can run Docker)
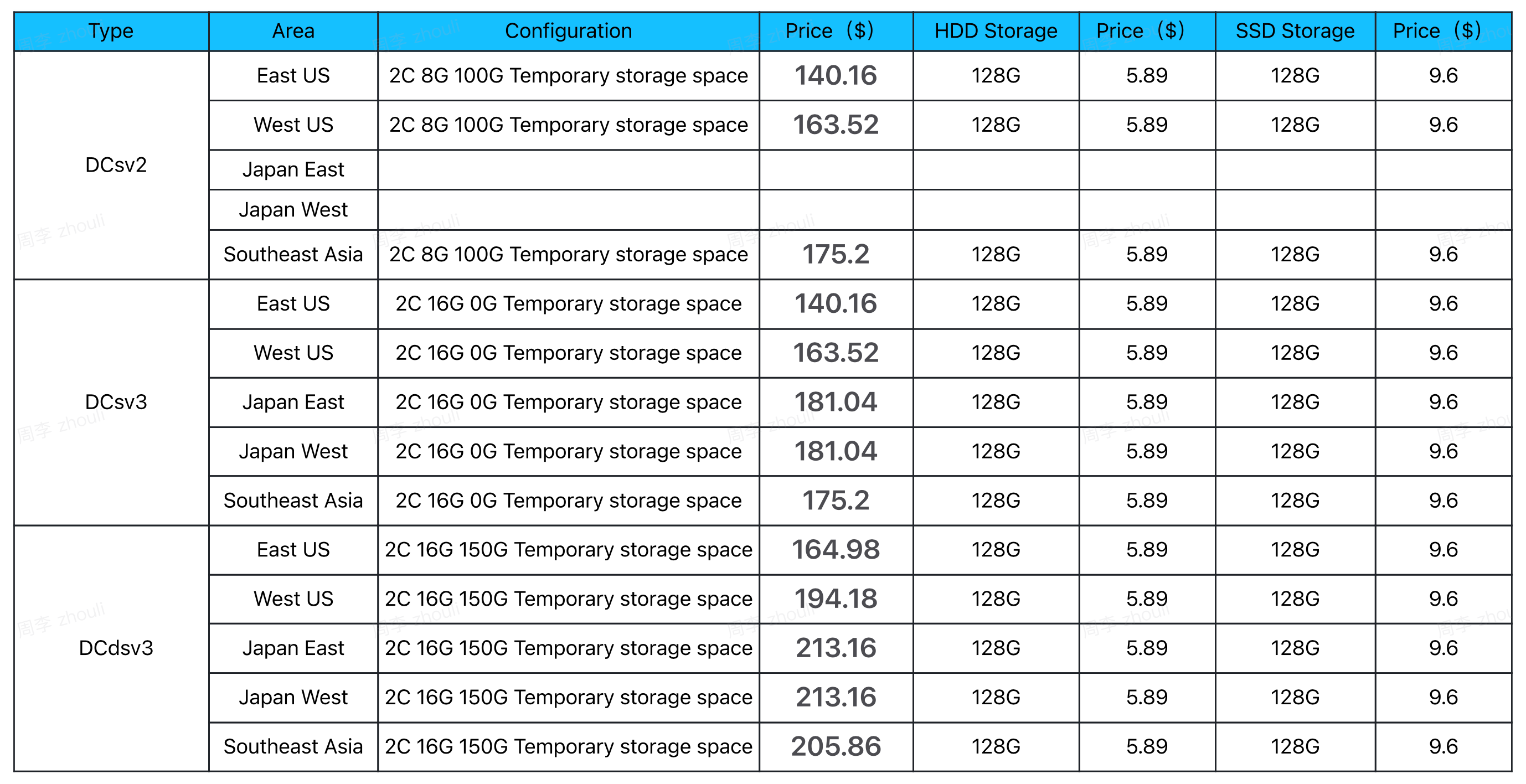
2.1.2 TEE server environment
You can refer to Azure's SGX Cloud as a Service to quickly complete the configuration of the machine, Quick Start: Create an Intel SGX VM in the Azure Marketplace . When purchasing a Microsoft Cloud SGX server, please select Ubuntu 20.04 and DCsv3 series support standards. For configuration instructions, please refer to: Solutions on Azure for Intel SGX .
Minimum configuration
- CPU: Intel-SGX architecture, 2 cores
- Memory: 4G
- Hard drive: 64G SSD
- Operating System: Ubuntu 20.04
Recommended configuration
CPU: Intel-SGX architecture, 2 cores
Memory: 16 G
Hard drive: 128G SSD
Operating system: Ubuntu 20.04 or latest. (Note: Theoretically supports all systems that can run Docker)
Check the machine's support for SGX if Azure Cloud as a Service is already configured by default.
apt install cpuid
cpuid | grep SGX
- Check the SGX driver installation if Azure Cloud as a Service is configured by default.
If your system supports FLC, make sure your Linux kernel version is 5.11 or higher. You can check with uname -r. If you are unable to upgrade the kernel, you can install the DCAP driver.
ls /dev/*sgx*
2.1.3 network requirements
Firewall inbound rules
- Open port 443, MPC Node service provides HTTPS service to users.
- Turn off all other ports without affecting operation and security.
Firewall outbound rules
- Installation phase:
- Access to apt sources to install base dependencies
- Access docker installation source to install docker
- Access to docker.io registry mirroring repository
- Service phase:
- Access to client-configured callback servers
- Can access mpc-proxy, need to communicate with other MPC nodes when signing.
- Turn off all other outbound IPs without affecting operation and security.
2.1.4 install Docker
Please refer to the official documentation to install Docker. When the startup script in the Sinohope MPC Node installation package is executed, it will automatically check the installation status of Docker. If it is not installed, it cannot run.
2.2 Deployment and configuration
Deploying and configuring MPC Node is a basic requirement for using Sinohope WaaS service. Please refer to the following steps to complete the deployment and operation of MPC Node.
- Prepare: Open Sinohope WaaS account; Prepare deployment environment, obtain and verify MPC Node installation package.
- Initialize the node, generate the node ID and the node public key required for deploying the callback service.
- (On demand) Deploy and configure your callback service;
- Bind MPC Node, log in to the web console to configure MPC Node, and bind your Node ID with your organization account.
- Start MPC Node, the node will continue to run and automatically drive the operation of MPC protocol as needed. DKG will be completed after a moment, and then the "key share status" will be "generated" in the Web Console MPC Node management interface.
- ❗️❗️ important: back up MPC Node local database files safely and properly!
2.2.1 get and verify the installation package
- Software packages (mainly management scripts and configuration files) are released through open source projects. Download link: sinohope-mpc-node/releases. The programs located under
env/generalare used in the normal CPU environment, and the programs located underenv/intel-sgxare used in the Intel sgx CPU environment. - The Releases page will contain the sha256 value of the main content. Please check the consistency of the hash value after downloading the content to the target location.
The required initial files are as follows:
sinohope-mpc-node
├── config.toml (Configuration File)
└── node.sh (Manage Scripts)
- The node.sh script is used to control the behavior of the mpc-node service, such as generating shard private keys, starting services, etc. Executing
./node.sh helpwill get instructions for all commands. - The config.toml example and description are as follows:
[app]
# The name of the software is reflected in the log.
name = "mpc-node"
# 3 shards, a, b, c. Cannot be modified.
party-id = "a"
# User type, cannot be modified.
account-type = "2"
# log
[log]
# Log level: 0: Panic 1: Fatal 2: Error 3: Warn 4: Info 5: Debug 6: Trace
[log.stdout]
# Whether to enable terminal log output
enable=true
# Log level
level=6
[log.file]
# Whether to enable file log output
enable=true
# Log level
level=6
# The log file path is the internal path of docker. When node.sh start is executed, the current directory will be mapped to /tmp/mpc-node in docker.
path = "/tmp/mpc-node/logs/mpc-node.log"
# Shard storage
[storage]
# Storage engine type, divided into bolt and sgx, the default is bolt. Bolt is file database storage, and sgx is text file storage. If using the intel-sgx-tee environment, it must be specified as sgx storage.
engine = "bolt"
# t/n The combined password can be a 1/1 password or a 2/3 password. Just enter any two passwords. If t>1, the password must be generated by a special tool and cannot be generated freely.
t=1
n=1
# The fragmented data storage path is the internal path of docker.
db-file-path = "/tmp/mpc-node/asset.db"
# The service address and port are the internal address and port of docker.
unseal-server-address = "0.0.0.0:8080"
# mpc server is responsible for connecting three mpc nodes.
[mpc-service]
# node needs to use websocket to establish a connection with mpc server
protocol = "wss" .
#URL address of mpc server
address = "api.sinohope.com"
# URL path of mpc server
path = "/proxy"
# Encryption of "signature result", mpc encrypts the raw_data signature result once, so that others cannot use it even if they get the signature result.
[encrypt-signature]
# Whether to enable
enable=true
# The Secp256r1 public key path used for encryption is the internal path of docker.
public-key-path = "/tmp/mpc-node/encrypt_sig_public.pem"
# Signature callback service. Before signing, mpc-node sends the data to be signed to the callback service, and the callback checks whether the signature is allowed.
[callback]
retry-times=60
sleep-seconds = 60
# callback list, if the list is empty, the callback will not take effect.
[[callback.server]]
# callback address
address = "http://10.151.100.41:9090"
# The result returned by mpc-node calling callback is signed using the Secp256r1 private key. mpc-node verifies the correctness of the signature through the public key. The path of the public key is the internal path of docker.
public-key-path = "/tmp/mpc-node/callback_server_public.pem"
- After successful initialization of MPC Node, the asset.db file and logs directory will be automatically created.
sinohope-mpc-node
├── config.toml
├── node.sh
├── asset.db (Important locally generated data is stored here, and backup and recovery are the process of restoring data)
└── logs (Log file directory)
2.2.2 Initialize Node
First, execute the following command to start the mpc-node service. The service must be started before executing any other commands.
sudo ./node.sh start
示例:
./node.sh start
mpc-node instance name: mpc-node, unseal server address: 127.0.0.1:10080
a0c4e4380926d588016570a5d99a7b875a997c841d70472a4bcf1972b200ec49
mpc-node server address: 127.0.0.1:10080
Note: Firstly, the script will automatically perform some environmental checks, such as determining whether Docker is installed and determining user permissions. If you need to run multiple mpc-nodes simultaneously on the current system, you need to distinguish them in the form of directories. If you try to run multiple mpc-nodes in the same directory, only the first initialized node can run normally. If you want to run two mpc-nodes, their names are assumed to be mpc-node-a and mpc-node-b, then you need to create two directories, their names can be: mpc-node-a and mpc-node-b. Then copy the node.sh and config.toml files to the above two directories respectively.
When deploying MPC Node for the first time, please execute the following command on the command line and complete the initialization according to the prompts.
sudo ./node.sh init
Example:
./node.sh init
New password:
Retype new password:
{"data":{"node_id":"sinoMzA1OTMwMTMwNjA3MmE4NjQ4Y2UzZDAyMDEwNjA4MmE4NjQ4Y2UzZDAzMDEwNzAzNDIwMDA0MDdlMDgyNzA5OTU1NTUxMzljODExMzQ3YTBkZjVmZjVhYmY1ZmM1MTFiOWFiM2U0MWE5N2MwMDlkODA3OGY3ZTc1MzlhYjA2M2ZkNzczZTliOTJjZWU5MjI1ZTVhMTFhYmJjNzExOWRlNDkwYjNiMzZkNTM3MWFmZDRkYjBiYzI=","public_key":"-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----\nMFkwEwYHKoZIzj0CAQYIKoZIzj0DAQcDQgAEB+CCcJlVVROcgRNHoN9f9av1/FEb\nmrPkGpfACdgHj351OasGP9dz6bks7pIl5aEau8cRneSQs7NtU3Gv1NsLwg==\n-----END PUBLIC KEY-----\n"},"status":"ok"}
The main task of the init command is to initialize node information, including:
- Set a password for the MPC node This password is used to protect your private key sharding and other private data. Please keep it properly, do not leak it, and do a Safety Redundancy backup . The node will be required to enter the password when it starts up.
- Create a node ID. Each MPC node has a unique identifier ID. You will need to use this node ID to uniquely associate your MPC node with your WaaS organization account.
- Create an ECDSA key pair when communicating with the callback-server.
Password Instructions:
- The password must include uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters, with a length of at least 12 characters.
- For the sinohope-mpc-node password, it adopts the t-n combination method, where t must be less than or equal to n (e.g., for 2/3, only 2 segments of the password are required during initialization and unsealing).
- If
storage.tin the configuration is set to 1, the operation command only needs to be executed once, and the password can be manually created. - If
storage.tin the configuration is greater than 1, the operation command needs to be executed t times, and t-n passwords need to be generated using specialized tools and cannot be created arbitrarily. click to get the password generation tool - T-n passwords require manual modification of
storage.tandstorage.nin the config.toml file.
2.2.3 (Optional) Deploy and Configure Callback Service
MPC Node provides a callback mechanism for you to perform risk control, and this callback service is optional (in production environments, it is strongly recommended that you develop and deploy callback services).
After configuring the callback service for the MPC Node, the MPC Node will call back the specified interface before initiating any MPC business (such as signing), requesting authorization from the callback service for the current MPC business. Only when your callback service explicitly returns the ACCEPT status, will the MPC business begin to execute.
In addition, when you use the function of message signing or direct signing of the original data source, MPC Node will provide the signing result to you through the callback interface for your business use.
For details on the development, deployment, and configuration of callback services, please refer to the "MPC Node callback mechanism" section.
2.2.4 Bind MPC Node
After completing the previous steps, you can log in to Sinohope Web Console with an account with administrator privileges, and complete the association binding of MPC Node on the "Settings" - "MPC Node" page. Here, you need to enter the Node ID generated during MPC Node initialization.
2.2.5 unseal MPC Node service
After binding the MPC Node, start the MPC Node service with the following command.
sudo ./node.sh unseal
Example:
./node.sh unseal
? Enter current password:
{"data":"in-bkey success","status":"ok"}
After the service starts running, return to the web console MPC Node configuration interface. Normally, wait a moment to see the "key share status" as "generated". At the same time, the interface will display your organization's MPC root public key information.
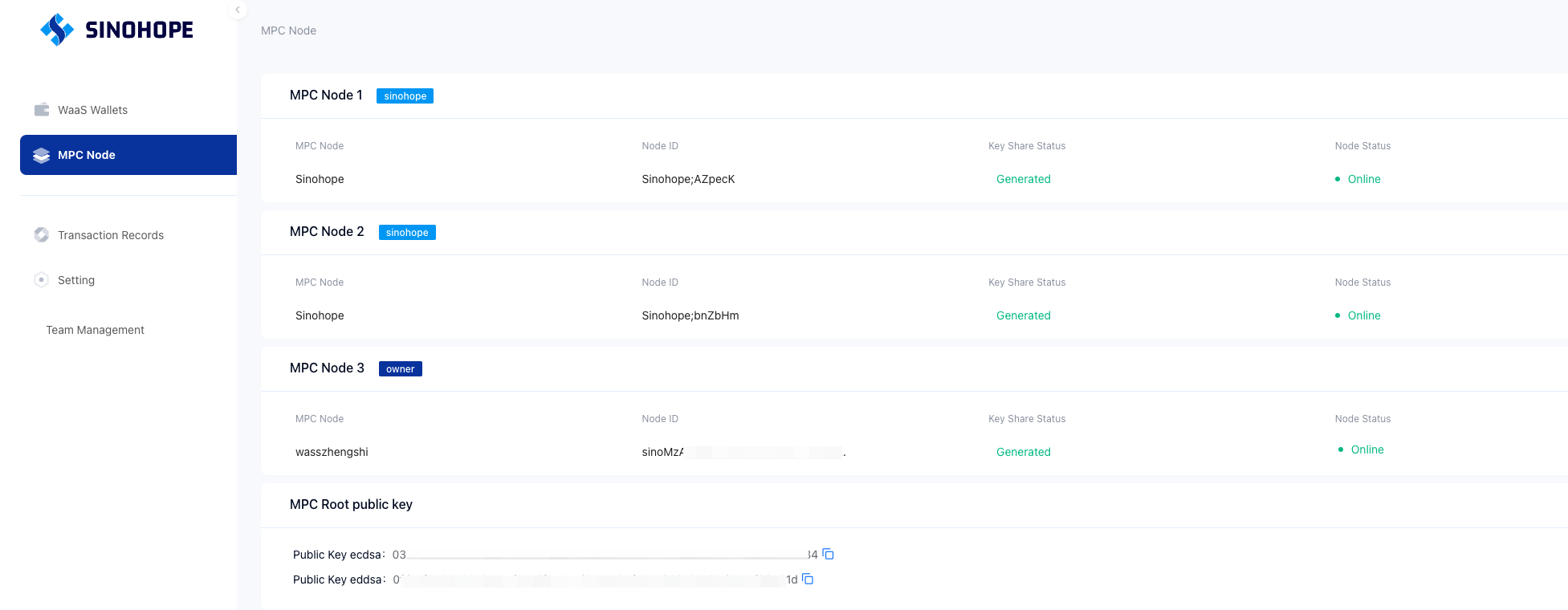
2.2.6 ❗️❗️ important: database backup
The MPC Node local database file asset.db stores important data such as your private key sharding, all encrypted using a strong key derived from the password you set for MPC Node via the KDF function.
Private key sharding is related to the security and availability of funds. The private key sharding managed by Sinohope is safeguarded and backed up by a series of highly available and disaster recovery solutions based on multi-level and multi-region platforms. At the same time, you can also apply for backup of all sharding private keys of your organization, thus fully controlling all three sharding private keys.
And for the private key sharding that exists in your local database file, you must complete the Safety Redundancy backup by yourself. Please take sufficient security measures, remote multiple copies, backup your database file, and the password you set for MPC Node.
It is recommended that database files be kept separate from passwords to reduce the risk of data leakage.
If your MPC Node server or service fails, data is damaged, or becomes unavailable in the future, you can only restore it by redeploying the MPC Node service with the database, files, and passwords you backed up. Sinohope will not be able to help you restore your MPC Node service!!
3. MPC Node complete interactive command introduction
Start
Please execute the following command in the command line:
sudo ./node.sh start
Example:
./node.sh start
mpc-node instance name: mpc-node, unseal server address: 127.0.0.1:10080
a0c4e4380926d588016570a5d99a7b875a997c841d70472a4bcf1972b200ec49
mpc-node server address: 127.0.0.1:10080
Initialization
Please execute the following command in the command line:
sudo ./node.sh init
Example:
./node.sh init
New password:
Retype new password:
{"data":{"node_id":"sinoMzA1OTMwMTMwNjA3MmE4NjQ4Y2UzZDAyMDEwNjA4MmE4NjQ4Y2UzZDAzMDEwNzAzNDIwMDA0MDdlMDgyNzA5OTU1NTUxMzljODExMzQ3YTBkZjVmZjVhYmY1ZmM1MTFiOWFiM2U0MWE5N2MwMDlkODA3OGY3ZTc1MzlhYjA2M2ZkNzczZTliOTJjZWU5MjI1ZTVhMTFhYmJjNzExOWRlNDkwYjNiMzZkNTM3MWFmZDRkYjBiYzI=","public_key":"-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----\nMFkwEwYHKoZIzj0CAQYIKoZIzj0DAQcDQgAEB+CCcJlVVROcgRNHoN9f9av1/FEb\nmrPkGpfACdgHj351OasGP9dz6bks7pIl5aEau8cRneSQs7NtU3Gv1NsLwg==\n-----END PUBLIC KEY-----\n"},"status":"ok"}
Unseal the service
Please execute the following command in the command line:
./node.sh unseal
Example:
./node.sh unseal
? Enter current password:
{"data":"in-bkey success","status":"ok"}
Note: The script will read the password and start the service in docker
MPC Node Other Commands
Note: The main commands to start the service are init and start. Other commands are optional and can be consulted as needed.
View node-id and callback public key
This command can view the MPC Node ID and callback service communication public key, and can only be used when the MPC Node is running.
./node.sh info
Example:
./node.sh info
{
"data": {
"node_id": "sinoMzA1OTMwMTMwNjA3MmE4NjQ4Y2UzZDAyMDEwNjA4MmE4NjQ4Y2UzZDAzMDEwNzAzNDIwMDA0MmFmNGY0Y2I5ZmM1MGFjMWUzNzIxMzM2Y2IyMmJmYzMzMDg4YjJmNGM4OTEyZjZhNDE4ZmNlY2JmZWFhMzIwMjNlMzg0MGE1YjBkODI3YWE5ODE1N2Y1MTE5Y2M2YTdiYzQ2NWNmN2EzNzc0MTkwNjdmYzc5ZGNjMjQ0YjgxZTU=",
"public_key": "-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----\nMFkwEwYHKoZIzj0CAQYIKoZIzj0DAQcDQgAEKvT0y5/FCsHjchM2yyK/wzCIsvTI\nkS9qQY/Oy/6qMgI+OEClsNgnqpgVf1EZzGp7xGXPejd0GQZ/x53MJEuB5Q==\n-----END PUBLIC KEY-----\n",
"state": "unsealed"
},
"status": "ok"
}
Change password
This command is used to modify the MPC Node password. Enter old password, Please make sure that the MPC Node is in normal operation (complete MPC Node binding, and the node is online normally).
./node.sh reset
Example:
./node.sh reset
? Enter current password:
{"data":"re-bkey-init success","status":"ok"}
This command is used to modify the MPC Node password. Enter a new password, Please make sure that the MPC Node is in normal operation (complete MPC Node binding, and the node is online normally).
./node.sh cmreset
示例:
./node.sh cmreset
New password:
Retype new password:
{"status": "ok", "data": "re-bkey success"}
Stop service
./node.sh stop
Manually check the environment
./node.sh check
Command to help
./node.sh help
4. MPC Node callback mechanism
After starting up, MPC Node will automatically establish a long link with Sinohope backend to receive tasks sent by Sinohope backend. By default, MPC Node does not enable callback mechanism, and MPC Node will automatically complete the execution of all tasks.
If the callback mechanism is enabled, the customer needs to develop a callback verification service to verify whether the tasks issued by Sinohope are reasonable and ultimately decide whether to cooperate with Sinohope to complete the signature.
The development of callback service can refer to the callback service example provided by Sinohope: GitHub - sinohope/mpc-node-callback-demo
4.1 Configure the callback validation service
Some initialization configuration work needs to be done on the host where the callback server is deployed. The specific steps are as follows:
- Generate ECDSA private key for callback server
openssl ecparam -genkey -name prime256v1 -out private_key.pem
- Export the ECDSA public key of the callback server
openssl ec -in private_key.pem -pubout -out callback_server_public.pem
- Copy the exported ECDSA public key (i.e. callback_server_public file) to the machine where the MPC Node is located, and specify the location of the callback_server_public file in the MPC Node configuration file:
[callback]
retry-times = 60
sleep-seconds = 60
[[callback.server]]
address = "http://<callback url>"
public-key-path = "./callback_server_public.pem"
- Copy the MPC Node's ECDSA public key to the callback server related configuration file
How to obtain the ECDSA public key of MPC Node:
- After the initialization of MPC Node is completed, the ECDSA public key of MPC Node can be queried by the following command:
./node.sh info
- Example output:
./node.sh info
checking update...
{
"data": {
"node_id": "sinoMzA1OTMwMTMwNjA3MmE4NjQ4Y2UzZDAyMDEwNjA4MmE4NjQ4Y2UzZDAzMDEwNzAzNDIwMDA0MmFmNGY0Y2I5ZmM1MGFjMWUzNzIxMzM2Y2IyMmJmYzMzMDg4YjJmNGM4OTEyZjZhNDE4ZmNlY2JmZWFhMzIwMjNlMzg0MGE1YjBkODI3YWE5ODE1N2Y1MTE5Y2M2YTdiYzQ2NWNmN2EzNzc0MTkwNjdmYzc5ZGNjMjQ0YjgxZTU=",
"public_key": "-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----\nMFkwEwYHKoZIzj0CAQYIKoZIzj0DAQcDQgAEKvT0y5/FCsHjchM2yyK/wzCIsvTI\nkS9qQY/Oy/6qMgI+OEClsNgnqpgVf1EZzGp7xGXPejd0GQZ/x53MJEuB5Q==\n-----END PUBLIC KEY-----\n",
"state": "unsealed"
},
"status": "ok"
}
The public key is the ECDSA public key used by MPC Node for callback service.
4.2 Develop callback validation service
4.2.1 signature and verification
The data between MPC Node and callback service is signed by their respective ECDSA private keys, and then the other party uses the pre-configured public key to verify the signature according to the specified rules. Only when the signature is passed can it be considered a legitimate request.
The following is the data structure for communication between the current MPC Node and the callback service. Please be careful not to change the order of fields arbitrarily.
Request:
type Check struct {
CallbackId string `json:"callback_id,omitempty"`
RequestType string `json:"request_type,omitempty"`
RequestDetail `json:"request_detail,omitempty"`
ExtraInfo `json:"extra_info,omitempty"`
}
type RequestDetail struct {
T int `json:"t,omitempty"`
N int `json:"n,omitempty"`
Cryptography string `json:"cryptography,omitempty"`
PartyIds []string `json:"party_ids,omitempty"`
PublicKey string `json:"public_key,omitempty"`
Path string `json:"path,omitempty"`
Message string `json:"message,omitempty"`
Coin string `json:"coin,omitempty"`
FromAddress string `json:"from_address,omitempty"`
ToAddress string `json:"to_address,omitempty"`
Amount string `json:"amount,omitempty"`
Fee string `json:"fee,omitempty"`
GasPrice string `json:"gas_price,omitempty"`
GasLimit string `json:"gas_limit,omitempty"`
Signature string `json:"signature,omitempty"`
}
type ExtraInfo struct {
SinoId string `json:"sino_id,omitempty"`
RequestId string `json:"request_id,omitempty"`
}
Response:
type Response struct {
Status string `json:"status,omitempty"`
Error string `json:"error,omitempty"`
Data *ResponseData `json:"data,omitempty"`
Signature string `json:"signature,omitempty"`
}
type ResponseData struct {
CallbackId string `json:"callback_id,omitempty"`
SinoId string `json:"sino_id,omitempty"`
RequestId string `json:"request_id,omitempty"`
Action string `json:"action,omitempty"`
WaitTime string `json:"wait_time,omitempty"`
}
1. Generate Request Signature
- MPC Node constructs a Check structure based on the type of request.
- Serialize the constructed Check structure in JSON to obtain the Message.
- MPC Node uses its own ECDSA private key to sign the message and obtain the signature.
- MPC Node sets Signature to the HTTP request header, with Key as Sigature.
2. Request signature verification
- The callback service uses the Check structure to parse the HTTP request of the MPC Node and obtain the Check data of this request.
- The callback service serializes the Check data obtained in JSON to obtain the Message to be verified.
- The callback service obtains the Signature from the HTTP request, and then verifies the Signature by combining Mesage and the pre-configured MPC Node public key.
3. Generate Response Signature
- The callback service generates the above Response based on its own decision and fills the corresponding fields in the Response.Data.
- The callback service serializes the Response.Data in JSON to obtain the Message.
- The callback service uses its own ECDSA private key to sign the Message, obtains the Signature, and assigns the Signature to the Response. Signature field.
4. Response signature verification
- MPC Node receives the response of the callback service and serializes the Response.Data field in JSON to obtain the Message.
- MPC Node verifies Response. Signature by combining Message and pre-configured callback service public key.
4.2.2 check
Each time the keygen and sign business mpc-node will request the user for risk control through the check interface. Only when the callback service explicitly replies Approve can the relevant business be allowed to start.
1. HTTP interface
path: /check
method: post
Body: JSON-encoded data
2、Request
| 参数 | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| callback_id | string | callback request unique ID |
| request_type | string | callback request is a string type, there are six values: keygen, sign, pre-sign, pre-sign-online, bip340-schnorr-sign, taproot-sign |
| request_detail | struct | Callback request details, including a series of key information of the request. Different callback request types correspond to different request_detail structures; the format is JSON serialized string |
| extra_info | struct | callback request auxiliary information, including some additional relevant information of the request; format is JSON serialized string |
- When request_type == keygen , the request_detail structure is defined as follows:
| Parameters | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Threshold | int | signature threshold |
| party_ids | []string | Collection of node IDs involved in generating private keys |
| Cryptography | string | signature algorithm. ecdsa-secp256k1/eddsa-ed25519 |
- When request_type is sign or bip340-schnorr-sign or taproot-sign or pre-sign or pre-sign-online, the request_detail structure is defined as follows:
| Parameters | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| sign_type | string | Transaction type to be signed: 1. Ordinary transaction; 2. EIP191/EIP712 signature; 3. RawData signature; |
| public_key | string | public key corresponding to the root public key |
| path | string | bip32 derived path |
| message | string | message to be signed |
| tx_info | json | Transaction Details |
The structure of tx_info is defined as follows:
| Parameters | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VaultId | string | vault id |
| WalletId | string | wallet id |
| requestId | string | requestId of the requestor transaction |
| chainSymbol | string | chain identifier |
| AssetId | string | asset id |
| From | string | from address |
| To | string | to address |
| toTag | string | transaction memo |
| Amount | string | amount |
| Fee | string | handling fee, for transactions on non-EVM compatible chains of UTXO class, self-set fee, if |
| gasPrice | string | gasprice |
| gasLimit | string | gaslimit |
| Inputdata | string | Ethereum transaction data |
| note | string | note: Some remarks information that users need. |
| curInputId | string | inputId of signature data |
| tapScriptRoot | string | The tree root of taproot script |
| publickKey | string | The public key of the from address |
| extraData | json | Detailed data of utxo transactions, including vin, vout |
| brc20Details | json | brc20Details |
| runeDetails | json | runeDetails |
| pre_sign_signature_id | string | preSign signature id |
- Structure example of brc20Details:
[
{
"method": "transfer",
"ticker": "helloworkd",
"quantity": "920769938",
"inscriptionId": "affabbd94763045fb4bc4****************************************0",
"step": 3,
"from": "1Bt84h23CKi****************",
"to": "bc1q53ss0p87****************"
}
]
- Structure example of runeDetails:
[
{
"fromAddress": "1Bt84h23CKi****************",
"toAddress": "bc1q53ss0p87****************",
"runeName": "HELLOWORLD",
"runeId": "2818544:3897",
"runeSpacedName": "HELLO•WORLD",
"runeAmount": "100",
"runeSymbol": "¤",
"runeDivisibility": 0
}
]
- Structure example of extraData:
{
"toTag": "TOTAG1637",
"vinList": [
{
"address": "mwTnMZzAvUzVCQKGkdcAHYW1sMnJCumbJL",
"amount": 1425593,
"blockHash": "0000000000000005f9c6962d86854e412bf0cc1d61b5849c0ac2f83d701007a8",
"blockHeight": 2583605,
"blockState": 1,
"blockTimeStamp": 1711441887,
"currency": "btc",
"id": 6909,
"state": 0,
"tag": "",
"transactionHash": "17b0378f551ddfda5d512a7304fdc0f33493f0429a479e243f3653d7dca0700e",
"voutIndex": 1
}
],
"voutList": [
{
"address": "mwTnMZzAvUzVCQKGkdcAHYW1sMnJCumbJL",
"amount": 22000
}
]
}
- extra_info structure is defined as follows:
| Parameters | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| sino_id | string | Sinohope's internal unique identifier for the business corresponding to the current signature, which is provided in the response when developers call waas APIs such as create_transfer . |
3、Response
| Parameters | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Status | string | status code, when the status code is 0, it indicates that the callback server is executing normally; when the status code is other values, it indicates that some abnormal situations occurred during the execution of the callback server |
| Error | string | Error message; When the return value of status is not 0, it represents the error message that appears internally in the callback server; When the status is 0 and the risk control result is REJECT, it represents the specific risk control rejection information. |
| Data | json | requested result data |
Data structure
| Parameters | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| callback_id | string | callback_id of this request |
| sino_id | string | sino_id of this request |
| request_id | string | request_id of this request |
| Action | string | Processing result of this request: Approve: Allow Reject: Reject Wait: Retry after waiting |
| wait_time | string | When action is Wait, this field is used to indicate how long the MPC Node needs to wait, in seconds |
rawdata_signature
Only when the sign_type of the sign service is 2 or 3 and the MPC Node signature is successful will the original message and signature result be reported to the callback service.
1. HTTP interface
path: /rawdata_signature
method: post
body: JSON-encoded data
2、 Request
| Parameters | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| callback_id | string | callback request unique ID |
| request_detail | struct | Callback request details, including a series of key information of the request. Different callback request types correspond to different request_detail structures; the format is JSON serialized string |
| extra_info | struct | callback request auxiliary information, including some additional relevant information of the request; different callback request types correspond to different extra_info structures; the format is JSON serialized string |
request_defailt as follows:
| Parameters | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Message | string | Original message to be signed |
| Signature | string | signature result |
- extra_info structure is defined as follows:
| Parameters | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| sino_id | string | Sinohope's internal unique identifier for the business corresponding to the current signature, which is provided in the response when developers call waas APIs such as create_transfer . |
| request_id | string | The request ID passed in by the user through the WaaS interface. If the request is not a WaaS interface, Sinohope will automatically generate it internally |
3、Response
| Parameters | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Status | string | status code, when the status code is 0, it indicates that the callback server is executing normally; when the status code is other values, it indicates that some abnormal situations occurred during the execution of the callback server |
| Error | string | Error message; When the return value of status is not 0, it represents the error message that appears internally in the callback server; When the status is 0 and the risk control result is REJECT, it represents the specific risk control rejection information. |
4.3 Activate callback verification service
After the callback validation service is configured and started, you need to call./node.sh start to restart the MPC Node.
5. MPC Node Signature Result Encryption
For users deploying an independent mpc-node, the mpc-node can encrypt the signature result when calling the /v1/waas/mpc/web3/sign_message and /v1/waas/mpc/wallet/advance/sign_raw_data interfaces for signing.
- Encryption uses the Secp256r1 algorithm, with public key encryption and private key decryption.
- When user query the signature result using the interface
/v1/waas/mpc/web3/sign_result, they need to decrypt it before using it. - If the mpc-node is configured with a Callback callback service, the signature results received by the callback service also need to be decrypted before use.
5.1 Generating Encryption Public and Private Keys
openssl ecparam -genkey -name prime256v1 -out decrypt_sig_pirvate.pem
openssl ec -in decrypt_sig_pirvate.pem -pubout -out encrypt_sig_public.pem
5.2 Setting up the Configuration File
Enable signature result encryption in the config.toml configuration file and specify the public key for encryption.
[encrypt-signature]
enable=true
public-key-path = "/tmp/mpc-node/encrypt_sig_public.pem"
- If
encrypt-signature.enable = true, the mpc-node will encrypt the signature result; otherwise, it returns the original signature result.encrypt-signature.public-key-pathis the public key for encrypting the signature result, in PEM format. callback.server.public-key-pathis used for data verification between the mpc-node and the Callback service. The Callback service signs the communication data with a private key, and the mpc-node verifies the data using this public key, in PEM format.- Both
encrypt-signature.public-key-pathand `callback.server.public-key-path`` use the Secp256r1 algorithm. For simplicity, it is recommended to use the same public-private key pair.
5.3 Decrypt the signature result
In the callback service demo, decryption processing is performed on the callback result (encrypted signature data), which can be referred to in the callback service example provided by Sinohope: GitHub - sinohope/mpc-node-callback-demo
5.4 pre-sign
The MPC signature consumes a CPU and it takes time. Generally, a single signature may take 3-5 seconds to complete. The length of time depends on the performance and network conditions of the MPC-Node. If you want to get a millisecond experience, you can start the pre-sign. After opening, the system will make pre-sign when MPC-Node is free, and use the pre-sign-data before when signing the transaction.
- Preparation before the pre-sign: Signature Callback service supports two types of business types that support Request_type as Pre-Sign and Pre-Sign-Online.
- How to enable pre-sign strategy: At present, you need to contact the administrator, and the administrator will be assisted to use it